
Infusion and Biologic Therapies
Veros Health provides comprehensive therapy management for patients requiring specialty biologic medications.
With our Interdisciplinary Approach, Veros Health is committed to collaborating with your physician and other healthcare providers to ensure a safe course of therapy that meets the goals agreed upon by you, your physicians, and your Veros Health team.
Flexible Sites of Care
We offer a variety of site of care options for patients based upon the most clinically appropriate and cost-effecting setting.
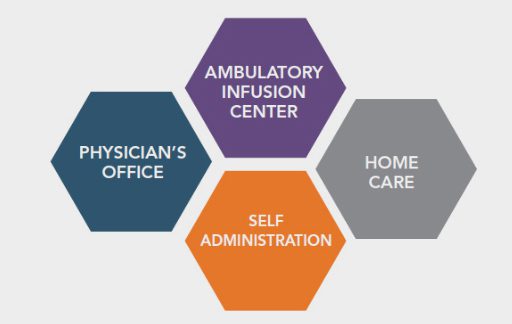

Ambulatory Infusion Center

- Experienced infusion provider present during infusions
- Highly trained and educated staff
- Flexible scheduling, including Saturday and evening appointments
- Comprehensive patient and caregiver education and support
- Coordination of infusion services with your prescribing physician
- Treatment for high-risk patients
- 24/7 access to on-call answering services
Biologic Therapies
Different biologic therapies have different purposes, targets, and design, and they all work a little differently. Some of the most common biologics are used for treating autoimmune diseases–diseases in which the body’s immune system plays a role in attacking its own tissue. These include conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease, to name a few.

Many of these therapies are approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat more than one type of autoimmune disease. In some cases, doctors may prescribe these treatments even if they haven’t been approved if they have seen evidence that the biologic was effective. This is known as off-label use.
Some of the General Classes of Biologics Include:
- Blood or other blood products (like platelets), intravenous immunoglobulin, subcutaneous immunoglobulin, and angioedema therapy
- Vaccines (for disease prevention)
- Recombinant nucleic acids (such as those developed for genetic hypercholesterolemia)
- Interleukins (immune molecules that can be used to treat certain autoimmune diseases)
- Monoclonal antibodies (like those used to treat autoimmune)

Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIg)
Immunoglobulin (Ig) therapy is a safe and effective way to treat several autoimmune diseases. Made from the blood plasma of carefully screened healthy adults, this therapy is infused into the body to replace antibodies that are often missing in people with autoimmune diseases.
Intravenous Immune Globulin
Intravenous immune globulin (“IVIg”) is a product made up of antibodies created naturally by the immune system that can be given through a vein via a drip. The immunoglobulins, provided by different donors to treat various conditions, help fight infection and disease.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) therapy is increasingly used in autoimmune diseases. Although its effectiveness has only been established in a few autoimmune conditions, accumulating evidence on its effectiveness in other autoimmune diseases makes it an attractive potential therapeutic option for clinical immunologists.
Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin Therapy
Rather than administered intravenously, immunoglobulin therapy can be administered subcutaneously.
When immunoglobulin is infused intravenously, it is usually done at home or at a medical facility every 3 or 4 weeks. Using the subcutaneous method, immunoglobulin is self-administered using an infusion pump and a short needle.



This method is preferred by people who have weak or damaged veins, and by people who prefer to self-administer therapy on their own schedule in their own home.
